Nautilus Design
When the enclave starts, it exposes 3 HTTP endpoints:
-
/health_check: Checks that the enclave can reach the allowed external domains. It is used for debugging. -
/get_attestation: Returns the signed attestation document. It is used during on-chain registration. -
/process_data: Contains your custom logic. You will write the code for this yourself. This is the endpoint that your app frontend will hit.
Platform Configuration Registers (PCR)
Three SHA-384 hashes that describe the enclave's code and configuration.
-
PCR0: OS and boot environment
-
PCR1: Application code
-
PCR2: Runtime configuration (
run.sh, traffic rules)
If a single byte changes, then the PCR changes. This is how Sui confirms that the enclave is running the expected code.
What happens inside the enclave
Step 1: Enclave starts
It generates a new ephemeral keypair inside its isolated memory. The private key never leaves enclave while the public key is returned via /get_attestation.
Step 2: Enclave signs data
When process_data returns { response, signature }, then the enclave signs the data with signature = sign( response ) using the enclave private key.
Step 3: Move contract verifies signature
An on-chain Move contract checks that the signature matches public key of registered enclave, the PCRs are correct, and the timestamp is recent. If all checks pass, the computation is accepted.
The role of smart contracts
Move smart contracts do two things in this process:
- They register the enclave by storing PCR0/1/2, verifying the attestation document, and storing the enclave public key inside a shared object.
Example object types created by Move smart contracts include the EnclaveConfig object for the PCRs and the Enclave object for the public key and metadata.
- They verify signed responses. The Move app logic calls
verify_signature()inside the Nautilus Move library. If the call is valid, data is accepted and logic continues. This guarantees that the app only accepts data from a real, authenticated enclave.
Natilus workflows
Nautilus involves two main participants: app developers who build and deploy the system, and users who interact with it. The framework establishes a trust model that allows users to verify computations without trusting the developer.
Developer workflow
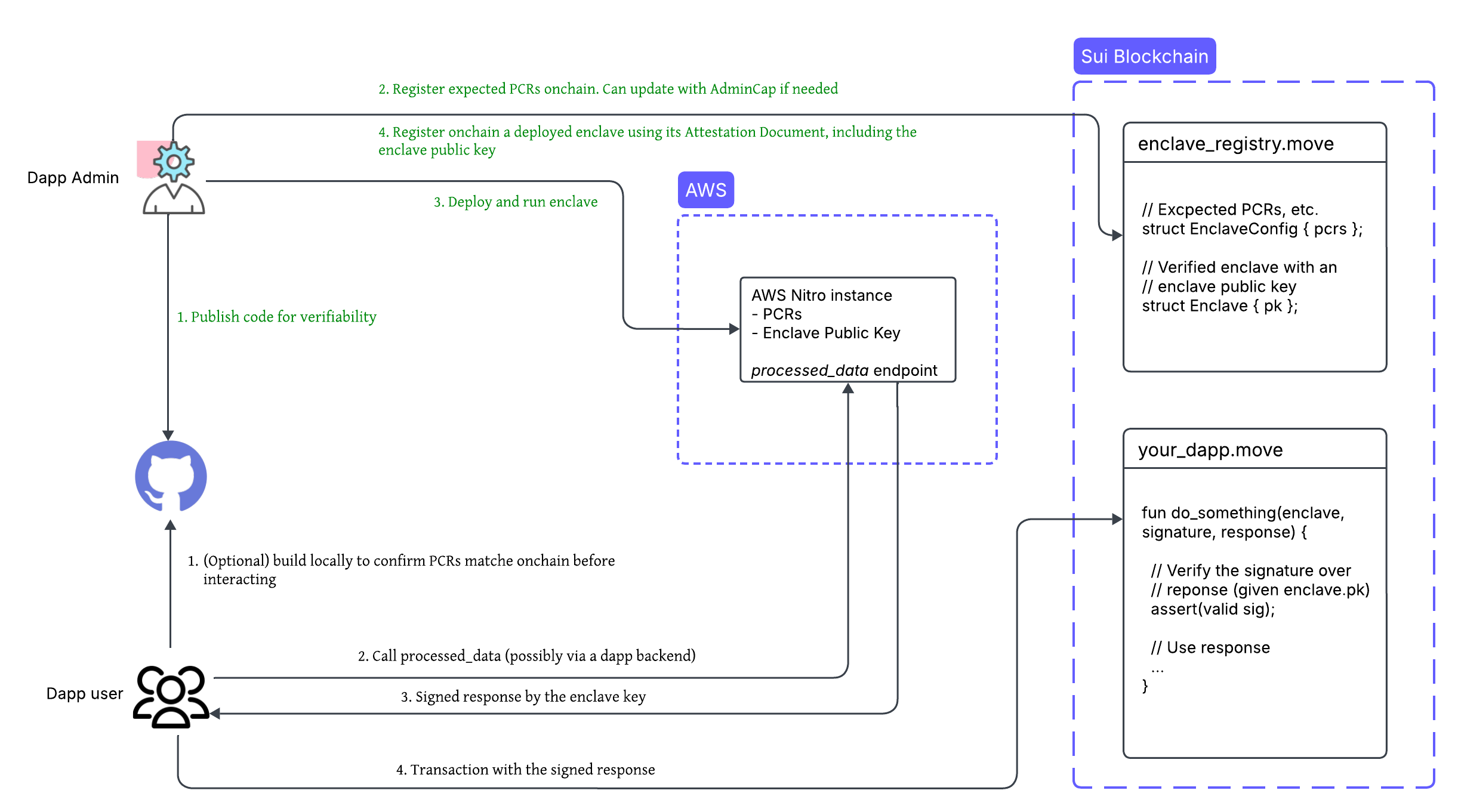
As an app developer, follow these steps to deploy an instance of Nautilus:
-
Create a Nautilus off-chain server with a reproducible build using the provided template.
-
Publish the server code to a public repository like GitHub to ensure transparency and verifiability.
-
Register the platform configuration registers (PCRs) of the instance. PCRs are measurements of the trusted computing base. Use a Sui smart contract to register them.
-
Deploy the server to an AWS Nitro Enclave.
-
Register the deployed enclave using a Sui smart contract and attestation document. Include the ephemeral public key of the enclave for signing responses.
Verify attestation documents on-chain only during enclave registration due to high gas costs. After registration, use the enclave key for more efficient message verification.
To reduce the trusted computing base, route access to the enclave through backend services that handle load balancing, rate limiting, and other related aspects.
User workflow
As a user or client application, you can verify and interact with a Nautilus enclave:
-
(Optional) Verify the Nautilus off-chain server code by building it locally and confirming that the generated PCRs match the on-chain records.
-
Send a request to the deployed enclave and receive a signed response.
-
Submit the signed response on-chain for verification before executing the corresponding application logic.
Trust model
The Nautilus trust model enables you to verify computations without trusting individual developers or service providers. This verification relies on cryptographic attestations and reproducible builds.
Attestation verification
The attestation document from an AWS Nitro Enclave includes a certificate chain that you can verify on-chain using AWS as the root certificate authority. This verification confirms:
-
The enclave instance is running unmodified software, as validated by its PCR values.
-
You can independently verify that the computation of the instance aligns with the published source code, ensuring transparency and trust.
Reproducible builds
Reproducible builds allow you to verify that the binary running inside an enclave instance matches a specific version of the source code. Reproducible builds might not apply to all use cases, such as when the source code is not public.
This approach provides the following benefits:
-
Anyone can build and compare the binary to confirm consistency with the published source code.
-
Any changes to the software result in different PCR values, making unauthorized modifications detectable.
-
Reproducible builds shift the trust from runtime to build time, strengthening the overall security posture of the app.
TEE security considerations
Nautilus uses cloud-based enclaves designed to protect against software-level attacks. Focusing on cloud-hosted TEEs, like AWS Nitro Enclaves, is intentional because cloud providers respond quickly to vulnerabilities. They receive early signals about security issues and can patch them efficiently. They also maintain strong physical security. Access to cloud data centers is tightly controlled, reducing the risk of physical hardware attacks. Lastly, they operate under strict compliance standards. Providers like AWS and GCP are regularly audited against frameworks like SOC 2, ISO 27001, CSA STAR, and others, ensuring operational integrity.
You are encouraged to evaluate whether this trust model aligns with the threat profile and security needs of your application.